Differences between Network latency and bandwidth
People often confuse the two. Network latency and bandwidth. Maybe everyone has mistakenly thought of one as the other at some point.
But, if downloading a file or sharing content over the internet is taking a bit too long on your network, it may not just have to do with internet speed.
That must be a relief to know when everybody brags about having a lightning-fast connection to the internet. But before we get to how network latency and bandwidth can be tested, let’s draw a clear line between the two.
Latency vs. Bandwidth
To put it simply, latency is the time taken for data to travel from one point to another. It is directly linked to the physical distance and the layer of networks, data must get through before it can be received at the two ends.
Bandwidth, on the other hand, is the rate of data transfer for a fixed amount of time.
Bandwidth can also be explained as the width of the channel through which the transferred data is flowing.
Hence, the larger the bandwidth, the more amount of data can go through at any given time.
While bandwidth can vary depending on the channel through which it is being supplied, such as broadband or optic fiber, the means of transmission will have no impact on network latency.
A better bandwidth increases the amount of data being relayed or being lost in transmission, the physical distance would remain the same.
With improving bandwidth speed due to the development of better transmission channels.
Latency is beginning to take more responsibility for slow download speeds and data transfer.
A lot of other factors contribute to making the two either better or worse.
But you get the idea. Let’s have a look at how you can calculate latency and bandwidth.
Effectively Measuring Latency and bandwidth
Both bandwidth and latency can be measured using open source tools available online.
But there are other means to figuring out how your internet connection is faring in these terms.
You can not only find out the speed of your downloads and connections but also find out what programs or files are consuming more bandwidth than others.
Using Command line to test bandwidth
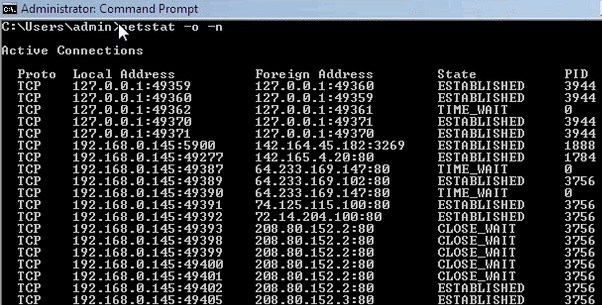
In Windows, you can use the Netstat command to determine which programs/websites are occupying large volumes of bandwidth when downloading files
- Run the command prompt as the administrator.
- In the Command Prompt, enter netstat -o -n and then press Enter.
- Under Active Connections, look at the PID (Process ID) column, and record any PID numbers that are repeated for many IP addresses. A PID with many connections may be using a lot of bandwidth.
4.Open the Windows Task Manager. And click the processes tab.
5.Put a checkmark beside PID (Process Identifier) and click OK.
6. In the process list, look for the PID(s) you noted in step
7.These would be associated with the programs consuming the most network speed. You can close these programs and test your internet connection.
Testing Network Latency using CMD
This is much simpler than the previous test. Once again, run cmd and ping the IP address of your server.

Look out for the ping statistics in the results that appear.
In the screenshot above, this is shown by the network round trip time in milliseconds and symbolizes the network latency speed.
The speed at which information has been relayed to and from a server or whatever IP address you type in.
You can use these tests to check the speeds of your at which data is exchanged from the website your server is hosted.
Along with various other means available online as well.




